What was Greece’s geography like? How did geography affect Ancient Greek
civilization?
Here’s a mystery box that will help us answer these
questions. The contents of this box
shaped Greek culture. It holds secret
weapons that helped Greece defeat the almost unstoppable Persian Empire. The items in this box also helped lead to the
fall of Ancient Greece.
The box contains…
- · A handful of large stones
- · Some rocky soil
- · Some trees (tiny ones – it’s a shoe box)
- · A bottle filled with salt water
Surprised? Believe it
or not, you just got a boxful of Ancient Greece! The contents of your mystery box represent
the geography of Ancient Greece. The
stones are mountains and islands. The
rocky soil, trees, and salt water are – you guessed it – rocky soil, trees, and
the ocean. When I learned this about
Ancient Greece, my first question was, “What the heck did they eat?”
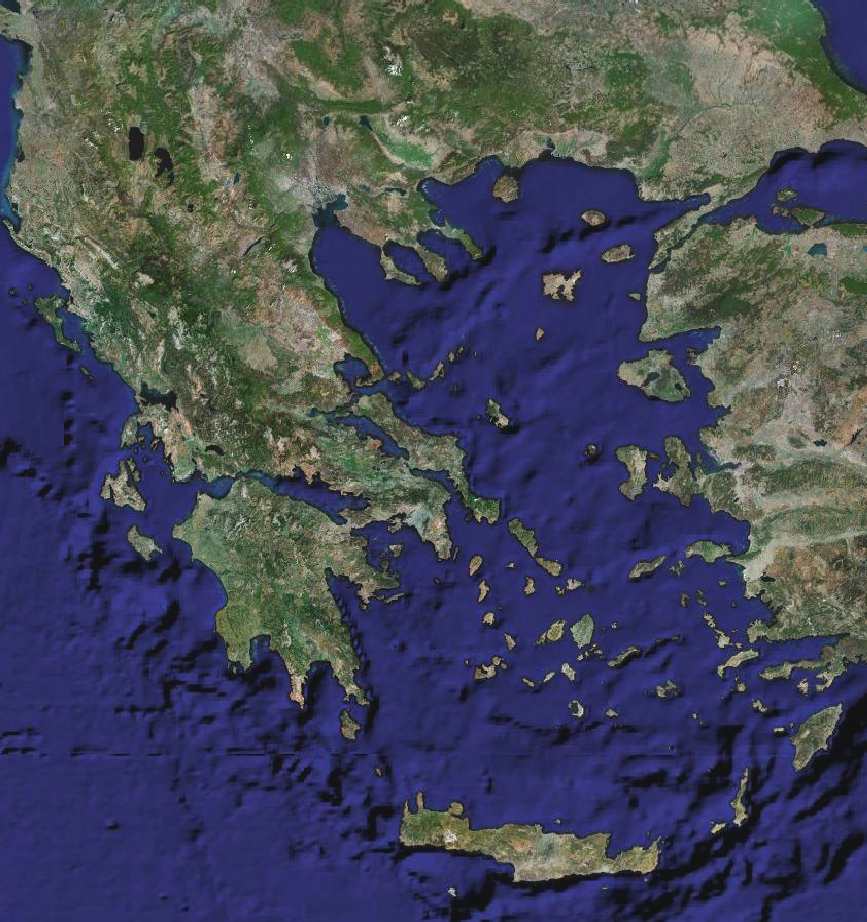 |
| Satellite Image of Greece (public domain) |
Naturally, the Greeks depended a lot on the sea for
food. However, about 1/3 of the land in
Greece was fertile enough to grow grains.
Barley was the Greek staple crop.
They also grew herbs such as mint and oregano, fruits like grapes,
apples, and pears, and vegetables such as onions, garlic, and chick peas. They raised goats and sheep for meat, wool,
and milk. Okay, that’s great, but was
this really enough to power one of the greatest civilizations of all time?
Well, yes and no. With
so little fertile land, the Greeks had to import grains from other
civilizations in the Eastern Mediterranean.
Fortunately, because most Greeks grew up near the ocean, they were great
sailors. The Ancient Greeks came to
dominate sea trade in the region. They
traded wood, olive oil - olive trees happen to love rocky soil – and other
products in order to get the resources they needed. They also established colonies throughout the
Mediterranean, wherever they could find a piece of available fertile land. Fertile land was as good as gold.
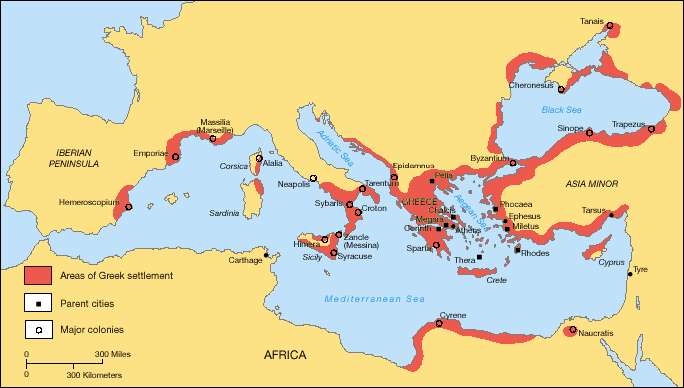 |
| Map of Greek Colonies (public pomain) |
Meanwhile, back in Greece, the Greek city-states were
isolated from each other by the mountains, forests, and the sea. Many city-states shared a religion, language,
and other customs, but they were also fiercely independent. There was no real sense that “we’re all
Greeks and we should work together.” The
city-states did their own thing. They
fought each other a lot, often over farmland, and they only really came
together for the Olympics and when they had to defeat the Persian invasion in the 400s BCE. Geography caused the
Greeks to fight each other, but it also played a huge part in their win over
the Persians.
Any outsider that wanted to invade Greece was in for a
surprise. In those times, armies usually
had to live off the land while they were away from home. As we’ve discussed, there was not much to
live off of in Greece. Even if an
invading army like the Persians had a sophisticated supply system for the army,
it would be hard to move it across the rugged terrain of Greece. Still, the Persians outnumbered the Greeks by
4 to 1 or more. Ah, yes, but geography
was on the Greek’s side.
The Persians were used to fighting on wide open plains with
cavalry and light, quick troops. These tactics did not work very well in Greece’s tight spaces and mountainous
terrain. The Greeks, very used to
fighting each other in Greece, had heavily armored troops that were well
trained slug it out in close fighting. Don’t
forget that the Greeks were great sailors too.
The Persians just sailed because they had to in order to get to
Greece. Using this “home field advantage”
provided by their own geography, the Greeks were able to defeat the Persian
Empire.
After the Persian Wars, the Greeks went back to living as
they had before. They went back to each
city-state doing its own thing and fighting each other. Ultimately, the Peloponnesian Wars were
fought between the Greek city-states, with Athens leading one side and Sparta
leading the other. Athens lost, and it
and the rest of Greece were never the same again. Weakened by decades of civil war, Greece eventually
fell to Alexander the Great and his father, Phillip II, in the 300s BCE.
The geography of Greece shaped its culture. It gave the Greeks much of what they needed
to thrive. It motivated trade and
colonization so they could get what they didn’t have enough of at home. Geography helped the Greeks triumph over the
mighty Persians. And yet, it also kept
them from becoming unified. What could
Greece have become? We will never
know. We do know, using the Greeks and
many other examples from ancient history, that geography has a huge influence
on how things turn out.
Now, put everything back in the mystery box. Give it to someone else and tell them how
some rocks, dirt, salt water, and trees helped shape the civilization of the
Ancient Greeks.
No comments:
Post a Comment